创建
入口
创建数据记录操作主要通过调用 gorm.DB 的 Create 方法完成,其包括如下核心步骤:
- 通过 db.getInstance() 克隆出一个 DB 会话实例
- 设置 statement 中的 dest 为用户传入的 dest
- 获取到 create 类型的 processor
- 调用 processor 的 Execute 方法,遍历执行 fns 函数链,完成创建操作
// Create inserts value, returning the inserted data's primary key in value's id
func (db *DB) Create(value interface{}) (tx *DB) {
// ...
// 克隆 db 会话实例
tx = db.getInstance()
// 设置 dest
tx.Statement.Dest = value
// 执行 create processor
return tx.callbacks.Create().Execute(tx)
}
在 create 类型 processor 的 fns 函数链中,最主要的执行函数就是 Create,其中核心步骤包括:
- 调用 statement.Build(…) 方法,生成 sql
- 调用 connPool.ExecContext(…) 方法,请求 mysql 服务端执行 sql(默认情况下,此处会使用 database/sql 标准库的 db.ExecContext(…) 方法)
- 调用 result.RowsAffected() ,获取到本次创建操作影响的数据行数
// Create create hook
func Create(config *Config) func(db *gorm.DB) {
supportReturning := utils.Contains(config.CreateClauses, "RETURNING")
return func(db *gorm.DB) {
// 生成 sql
if db.Statement.SQL.Len() == 0 {
db.Statement.SQL.Grow(180)
db.Statement.AddClauseIfNotExists(clause.Insert{})
db.Statement.AddClause(ConvertToCreateValues(db.Statement))
db.Statement.Build(db.Statement.BuildClauses...)
}
// ... 执行 sql
result, err := db.Statement.ConnPool.ExecContext(
db.Statement.Context, db.Statement.SQL.String(), db.Statement.Vars...,
)
// ... 获取影响的行数
db.RowsAffected, _ = result.RowsAffected()
// ...
}
}
删除
在 db.Delete 方法中,核心步骤包括:
- 通过 db.getInstance() 方法获取 db 的克隆实例
- 通过 statement.AddClause(…) 方法追加使用方传入的条件 condition
- 设置 statement dest 为使用方传入的 value
- 获取 delete 类型的 processor
- 执行 processor.Execute(…) 方法,遍历调用 fns 函数链
func (db *DB) Delete(value interface{}, conds ...interface{}) (tx *DB) {
tx = db.getInstance()
if len(conds) > 0 {
if exprs := tx.Statement.BuildCondition(conds[0], conds[1:]...); len(exprs) > 0 {
tx.Statement.AddClause(clause.Where{Exprs: exprs})
}
}
tx.Statement.Dest = value
return tx.callbacks.Delete().Execute(tx)
}
在 delete 类型的 processor 的 fns 函数链中,最核心的函数是 Delete,其中的核心步骤包括:
- 调用 statement.Build(…) 方法,生成 sql
- 倘若未启用 AllowGlobalUpdate 模式,则会校验使用方是否设置了 where 条件,未设置会抛出 gorm.ErrMissingWhereClause 错误(对应 checkMissingWhereConditions() 方法)
var ErrMissingWhereClause = errors.New("WHERE conditions required")
- 调用 connPool.ExecContext(…) 方法,执行删除操作(默认使用的是标准库 database/sql 中的 db.ExecContxt(…) 方法)
- 调用 result.RowsAffected() 方法,获取本次删除操作影响的数据行数
func Delete(config *Config) func(db *gorm.DB) {
supportReturning := utils.Contains(config.DeleteClauses, "RETURNING")
return func(db *gorm.DB) {
// ...
if db.Statement.Schema != nil {
for _, c := range db.Statement.Schema.DeleteClauses {
db.Statement.AddClause(c)
}
}
// 生成 sql
if db.Statement.SQL.Len() == 0 {
db.Statement.SQL.Grow(100)
db.Statement.AddClauseIfNotExists(clause.Delete{})
// ...
db.Statement.AddClauseIfNotExists(clause.From{})
db.Statement.Build(db.Statement.BuildClauses...)
}
// ...
checkMissingWhereConditions(db)
// ...
if !db.DryRun && db.Error == nil {
// ...
result, err := db.Statement.ConnPool.ExecContext(db.Statement.Context, db.Statement.SQL.String(), db.Statement.Vars...)
if db.AddError(err) == nil {
db.RowsAffected, _ = result.RowsAffected()
}
}
}
}
checkMissingWhereConditions 方法的源码如下:
func checkMissingWhereConditions(db *gorm.DB) {
// 倘若 AllowGlobalUpdate 标识不为 true 且 error 为空,则需要对 where 条件进行校验
if !db.AllowGlobalUpdate && db.Error == nil {
where, withCondition := db.Statement.Clauses["WHERE"]
// ...
// 不存在 where 条件,则需要抛出错误
if !withCondition {
db.AddError(gorm.ErrMissingWhereClause)
}
return
}
}
更新
在 db.Update 方法中,核心步骤包括:
- 通过 db.getInstance() 方法获取 db 的克隆实例
- 设置 statement dest 为使用方传入的 value
- 获取 update 类型的 processor
- 执行 processor.Execute(…) 方法,遍历调用 fns 函数链
func (db *DB) Updates(values interface{}) (tx *DB) {
tx = db.getInstance()
tx.Statement.Dest = values
return tx.callbacks.Update().Execute(tx)
}
在 update 类型 processor 的 fns 函数链中,最核心的函数就是 Update,其中核心步骤包括:
- 调用 statement.Build(…) 方法,生成 sql
- 和 Delete 流程类似,倘若未启用 AllowGlobalUpdate 模式,则会校验使用方是否设置了 where 条件,未设置会抛出 gorm.ErrMissingWhereClause 错误
- 调用 connPool.ExecContext(…) 方法,执行 sql(默认情况下,此处会使用 database/sql 标准库的 db.ExecContext(…) 方法)
- 调用 result.RowsAffected() 方法,获取到本次更新操作影响的行数
// Update update hook
func Update(config *Config) func(db *gorm.DB) {
supportReturning := utils.Contains(config.UpdateClauses, "RETURNING")
return func(db *gorm.DB) {
// ...
if db.Statement.Schema != nil {
for _, c := range db.Statement.Schema.UpdateClauses {
db.Statement.AddClause(c)
}
}
// 生成 sql
if db.Statement.SQL.Len() == 0 {
db.Statement.SQL.Grow(180)
db.Statement.AddClauseIfNotExists(clause.Update{})
// ...
db.Statement.Build(db.Statement.BuildClauses...)
}
// ... 校验 where 条件
checkMissingWhereConditions(db)
if !db.DryRun && db.Error == nil {
// ... 执行 sql
result, err := db.Statement.ConnPool.ExecContext(db.Statement.Context, db.Statement.SQL.String(), db.Statement.Vars...)
if db.AddError(err) == nil {
// 获取影响的行数
db.RowsAffected, _ = result.RowsAffected()
}
}
}
}
事务
- 调用 db.Transaction(…) 方法
- 传入闭包函数 fc,其中入参 tx 为带有事务会话属性的 db 实例,后续事务内所有执行操作都需要围绕这个 tx 展开
- 可以使用该 tx 实例完成事务的提交 tx.Commit() 和回滚 tx.Rollback() 操作
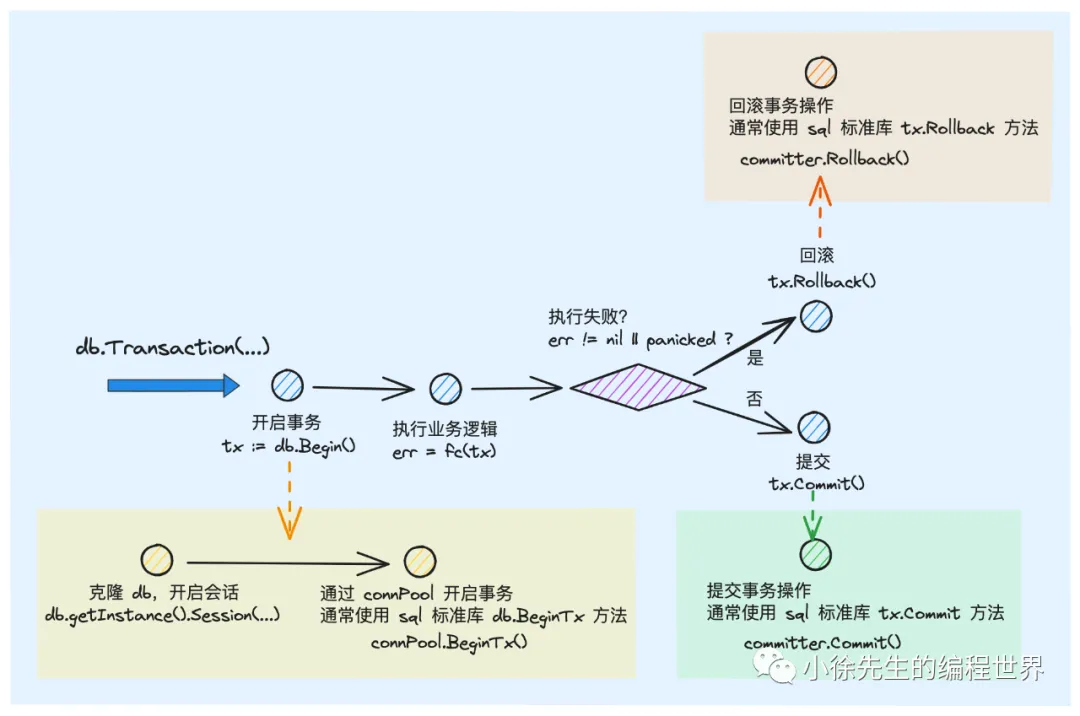
db.Transaction(…) 方法是启动事务的入口:
- 首先会调用 db.Begin(…) 方法启动事务,此时会克隆出一个带有事务属性的 DB 会话实例:tx
- 以 tx 为入参,调用使用方传入的闭包函数 fc(tx)
- 倘若 fc 执行成功,则自动为用户执行 tx.Commit() 操作
- 倘若 fc 执行出错或者发生 panic,则会 defer 保证执行 tx.Rollback() 操作
func (db *DB) Transaction(fc func(tx *DB) error, opts ...*sql.TxOptions) (err error) {
panicked := true
if committer, ok := db.Statement.ConnPool.(TxCommitter); ok && committer != nil {
// ...
} else {
// 开启事务
tx := db.Begin(opts...)
if tx.Error != nil {
return tx.Error
}
defer func() {
// 倘若发生错误或者 panic,则进行 rollback 回滚
if panicked || err != nil {
tx.Rollback()
}
}()
// 执行事务内的逻辑
if err = fc(tx); err == nil {
panicked = false
// 指定成功会进行 commit 操作
return tx.Commit().Error
}
}
panicked = false
return
}
开启事务
对于 DB.Begin() 方法,在默认模式下会使用 database/sql 库下的 sql.DB.BeginTx 方法创建出一个 sql.Tx 对象,将其赋给当前事务会话 DB 的 statement.ConnPool 字段,以供后续使用:
// Begin begins a transaction with any transaction options opts
func (db *DB) Begin(opts ...*sql.TxOptions) *DB {
var (
// clone statement
tx = db.getInstance().Session(&Session{Context: db.Statement.Context, NewDB: db.clone == 1})
opt *sql.TxOptions
err error
)
if len(opts) > 0 {
opt = opts[0]
}
switch beginner := tx.Statement.ConnPool.(type) {
// 标准模式,会走到 sql.DB.BeginTX 方法
case TxBeginner:
// 创建好的 tx 赋给 statment.ConnPool
tx.Statement.ConnPool, err = beginner.BeginTx(tx.Statement.Context, opt)
// prepare 模式,会走到 PreparedStmtDB.BeginTx 方法中
case ConnPoolBeginner:
// 创建好的 tx 赋给 statment.ConnPool
tx.Statement.ConnPool, err = beginner.BeginTx(tx.Statement.Context, opt)
default:
err = ErrInvalidTransaction
}
if err != nil {
tx.AddError(err)
}
return tx
}
提交/回滚
事务的提交和回滚操作,会执行 statement 中的 connPool 的 Commit 和 Rollback 方法完成:
- 执行事务提交操作:
// Commit commits the changes in a transaction
func (db *DB) Commit() *DB {
// 默认情况下,此处的 ConnPool 实现类为 database/sql.Tx
if committer, ok := db.Statement.ConnPool.(TxCommitter); ok && committer != nil && !reflect.ValueOf(committer).IsNil() {
db.AddError(committer.Commit())
} else {
db.AddError(ErrInvalidTransaction)
}
return db
}
- 执行事务回滚操作:
// Rollback rollbacks the changes in a transaction
func (db *DB) Rollback() *DB {
// 默认情况下,此处的 ConnPool 实现类为 database/sql.Tx
if committer, ok := db.Statement.ConnPool.(TxCommitter); ok && committer != nil {
if !reflect.ValueOf(committer).IsNil() {
db.AddError(committer.Rollback())
}
} else {
db.AddError(ErrInvalidTransaction)
}
return db
}
预处理
说白了就是可以复用stmt对象的缓存 然后直接对他执行操作 而不需要再次创建
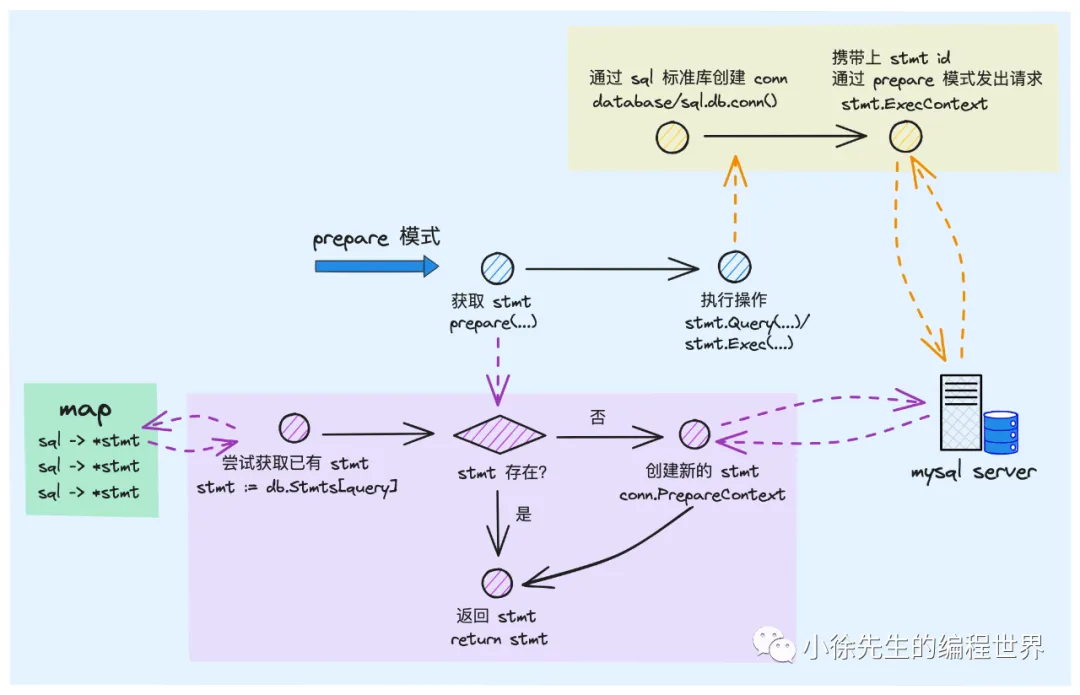
倘若创建 gorm.DB 时,倘若在 Config 中设置了 PrepareStmt 标识,则代表后续会启用 prepare 预处理模式. 此次在执行 query 或者 exec 操作时,使用的 ConnPool 的实现版本是 PreparedStmtDB,执行时会拆分为两个步骤:
- 通过 PreparedStmtDB.prepare(…) 操作创建/复用 stmt,后续相同 sql 模板可以复用此 stmt
- 通过 stmt.Query(…)/Exec(…) 执行 sql